5.3.3.6 IfcTask
5.3.3.6.1 Semantic definition
An IfcTask is an identifiable unit of work to be carried out in a construction project.
A task is typically used to describe an activity for the construction or installation of products, but is not limited to these types. For example it might be used to describe design processes, move operations and other design, construction and operation related activities as well.
Quantities of resources consumed by the task are dealt with by defining the IfcElementQuantity for the resource and not at the instance of IfcTask.
5.3.3.6.1.1 Attribute use definition
Each occurrence of IfcTask is given a name that is indicative of its content (IfcRoot.Name). A textual description of the task may be provided and this may be further elaborated by a narrative long description (IfcProcess.LongDescription). A work method may be declared for the method of work used in carrying out a task. A task is identified as being either a milestone task or not. A milestone task is defined by the marker IsMilestone. and has no duration. A status and priority for each task may also be set.
5.3.3.6.1.2 Time and duration use definition
Compared to previous IFC releases, basic task time information (scheduled start time, scheduled finish time, duration) is now directly attached to IfcTask through the TaskTime attribute. Regular tasks are defined through IfcTaskTime. Recurring tasks are defined through IfcTaskTimeRecurring. In case a regular task is derived from a recurring task both tasks should be linked together through a IfcRelNests relationship, where IfcRelNests.IsNestedBy points to the recurring task and IfcRelNests.Nests points to all regular tasks that have been derived from the recurring task.
5.3.3.6.1.3 Representation of other activities
The use definitions for IfcTask have been generalised to represent other activities as well, including activities that had been defined by own entities in previous IFC releases. This includes
- Order actions
- Move operations
IfcTask represents an order that might be carried out by a Helpdesk acting the role of interface for the organization between the facility user and the functional requirement of fulfilling their needs. The actual task represented by the IfcTask entity is turning a request into an order and initiating the action that will enable the order to be completed. The IfcProjectOrder or one of its subtypes including maintenance work order, is related to the IfcTask using IfcRelAssignsToControl.
IfcTask can also be used to describe an activity that moves people, groups within an organization or complete organizations together with their associated furniture and equipment from one place to another. It thus replaces the previous IFC entity IfcMove. The functionality is represented in IfcTask as follows:
- Move from: The place from which actors and their associated equipment are moving. Use IfcRelAssignsToProcess where RelatingProcess points to the task and RelatedObjects holds the location(s) from which to move.
- Move to: The place to which actors and their associated equipment are moving. Use IfcRelAssignsToProduct where RelatedObjects points to the task(s) and RelatingProduct points to the location to which to move.
- Punch list: A list of points concerning a move that require attention. Use LongDescription or else identify sub-tasks to track punch list items individually via IfcRelNests.
5.3.3.6.2 Entity inheritance
5.3.3.6.3 Attributes
| # | Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| IfcRoot (4) | |||
| 1 | GlobalId | IfcGloballyUniqueId |
Assignment of a globally unique identifier within the entire software world. |
| 2 | OwnerHistory | OPTIONAL IfcOwnerHistory |
Assignment of the information about the current ownership of that object, including owning actor, application, local identification and information captured about the recent changes of the object. |
| 3 | Name | OPTIONAL IfcLabel |
An optional name for use by the participating software systems or users. For some subtypes of IfcRoot the insertion of the Name attribute may be required. This would be enforced by a where rule. |
| 4 | Description | OPTIONAL IfcText |
An optional description, provided to exchange informative comments. |
| IfcObjectDefinition (7) | |||
| HasAssignments | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelAssigns FOR RelatedObjects |
Reference to the relationship objects, that assign (by an association relationship) other subtypes of IfcObject to this object instance. Examples are the association to products, processes, controls, resources or groups. |
|
| Nests | SET [0:1] OF IfcRelNests FOR RelatedObjects |
References to the decomposition relationship being a nesting. It determines that this object definition is a part within an ordered whole/part decomposition relationship. An object occurrence or type can only be part of a single decomposition (to allow hierarchical structures only). |
|
| IsNestedBy | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelNests FOR RelatingObject |
References to the decomposition relationship being a nesting. It determines that this object definition is the whole within an ordered whole/part decomposition relationship. An object or object type can be nested by several other objects (occurrences or types). |
|
| HasContext | SET [0:1] OF IfcRelDeclares FOR RelatedDefinitions |
References to the context providing context information such as project unit or representation context. It should only be asserted for the uppermost non-spatial object. |
|
| IsDecomposedBy | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelAggregates FOR RelatingObject |
References to the decomposition relationship being an aggregation. It determines that this object definition is the whole within an unordered whole/part decomposition relationship. An object definition can be aggregated by several other objects (occurrences or parts). |
|
| Decomposes | SET [0:1] OF IfcRelAggregates FOR RelatedObjects |
References to the decomposition relationship being an aggregation. It determines that this object definition is a part within an unordered whole/part decomposition relationship. An object definition can only be part of a single decomposition (to allow hierarchical structures only). |
|
| HasAssociations | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelAssociates FOR RelatedObjects |
Reference to the relationship objects, that associates external references or other resource definitions to the object. Examples are the association to library, documentation or classification. |
|
| IfcObject (5) | |||
| 5 | ObjectType | OPTIONAL IfcLabel |
The type denotes a particular type that indicates the object further. The use has to be established at the level of instantiable subtypes. In particular it holds the user defined type, if the enumeration of the attribute PredefinedType is set to USERDEFINED or when the concrete entity instantiated does not have a PredefinedType attribute. The latter is the case in some exceptional leaf classes and when instantiating IfcBuiltElement directly. |
| IsDeclaredBy | SET [0:1] OF IfcRelDefinesByObject FOR RelatedObjects |
Link to the relationship object pointing to the declaring object that provides the object definitions for this object occurrence. The declaring object has to be part of an object type decomposition. The associated IfcObject, or its subtypes, contains the specific information (as part of a type, or style, definition), that is common to all reflected instances of the declaring IfcObject, or its subtypes. |
|
| Declares | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelDefinesByObject FOR RelatingObject |
Link to the relationship object pointing to the reflected object(s) that receives the object definitions. The reflected object has to be part of an object occurrence decomposition. The associated IfcObject, or its subtypes, provides the specific information (as part of a type, or style, definition), that is common to all reflected instances of the declaring IfcObject, or its subtypes. |
|
| IsTypedBy | SET [0:1] OF IfcRelDefinesByType FOR RelatedObjects |
Set of relationships to the object type that provides the type definitions for this object occurrence. The then associated IfcTypeObject, or its subtypes, contains the specific information (or type, or style), that is common to all instances of IfcObject, or its subtypes, referring to the same type. |
|
| IsDefinedBy | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelDefinesByProperties FOR RelatedObjects |
Set of relationships to property set definitions attached to this object. Those statically or dynamically defined properties contain alphanumeric information content that further defines the object. |
|
| IfcProcess (5) | |||
| 6 | Identification | OPTIONAL IfcIdentifier |
An identifying designation given to a process or activity. It is the identifier at the occurrence level. |
| 7 | LongDescription | OPTIONAL IfcText |
An extended description or narrative that may be provided. |
| IsPredecessorTo | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelSequence FOR RelatingProcess |
Dependency between two activities, it refers to the subsequent activity for which this activity is the predecessor. The link between two activities can include a link type and a lag time. |
|
| IsSuccessorFrom | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelSequence FOR RelatedProcess |
Dependency between two activities, it refers to the previous activity for which this activity is the successor. The link between two activities can include a link type and a lag time. |
|
| OperatesOn | SET [0:?] OF IfcRelAssignsToProcess FOR RelatingProcess |
Set of relationships to other objects, e.g. products, processes, controls, resources or actors, that are operated on by the process. |
|
| Click to show 21 hidden inherited attributes Click to hide 21 inherited attributes | |||
| IfcTask (6) | |||
| 8 | Status | OPTIONAL IfcLabel |
Current status of the task. |
| 9 | WorkMethod | OPTIONAL IfcLabel |
The method of work used in carrying out a task. |
| 10 | IsMilestone | IfcBoolean |
Identifies whether a task is a milestone task (= TRUE) or not (= FALSE). |
| 11 | Priority | OPTIONAL IfcInteger |
A value that indicates the relative priority of the task (in comparison to the priorities of other tasks). |
| 12 | TaskTime | OPTIONAL IfcTaskTime |
Time related information for the task. |
| 13 | PredefinedType | OPTIONAL IfcTaskTypeEnum |
Identifies the predefined types of a task from which the type required may be set. |
5.3.3.6.4 Formal propositions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CorrectPredefinedType |
The attribute ObjectType must be asserted when the value of PredefinedType is set to USERDEFINED. |
|
|
| HasName |
The Name attribute should be inserted to describe the task name. |
|
|
5.3.3.6.5 Property sets
-
Pset_PackingInstructions
MOVE- PackingCareType
- WrappingMaterial
- ContainerMaterial
- SpecialInstructions
-
Pset_Risk
- RiskName
- RiskType
- NatureOfRisk
- RiskAssessmentMethodology
- UnmitigatedRiskLikelihood
- UnmitigatedRiskConsequence
- UnmitigatedRiskSignificance
- MitigationPlanned
- MitigatedRiskLikelihood
- MitigatedRiskConsequence
- MitigatedRiskSignificance
- MitigationProposed
- AssociatedProduct
- AssociatedActivity
- AssociatedLocation
5.3.3.6.6 Concept usage
| Concept | Usage | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IfcRoot (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revision Control | General |
Ownership, history, and merge state is captured using IfcOwnerHistory. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software Identity | General |
IfcRoot assigns the globally unique ID. In addition, it may also provide a name and description for the concept. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IfcObjectDefinition (9) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Classification Association | General |
Any object occurrence or object type can have a reference to a specific classification reference, i.e. to a particular facet within a classification system. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregation | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Approval Association | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constraint Association | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Document Association | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Library Association | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Association | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Single | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nesting | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IfcObject (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Object Predefined Type | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Object Typing | General |
Any object occurrence can be typed by being assigned to a common object type utilizing this concept. A particular rule, restricting the applicable subtypes of IfcTypeObject that can be assigned, is introduced by overriding this concept at the level of subtypes of IfcObject. This concept can be applied to the following resources: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Object User Identity | General |
An attribute Name and optionally Description can be used for all subypes of IfcObject. For those subtypes, that have an object type definition, such as IfcBeam - IfcBeamType, the common Name and optionally Description is associated with the object type. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Property Sets with Override | General |
Any object occurrence can hold property sets, either directly at the object occurrence as element specific property sets, or at the object type, as type property sets. In this case, the properties that are provided to the object occurrence are the combinations of element specific and type properties. In case that the same property (within the same property set) is defined both in occurrence and type properties, the property value of the occurrence property overrides the property value of the type property. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assignment to Group | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IfcProcess (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Property Sets for Objects | General |
This concept can be applied to the following resources: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Object Typing | General |
This concept can be applied to the following resources: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Process Assignment | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sequential Connectivity | General |
No description available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Click to show 20 hidden inherited concepts Click to hide 20 inherited concepts | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IfcTask (7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Classification Association | General |
An IfcTask may be assigned a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) code from of a published external structure or company standard. As well as being used to designate the code, the classification structure also enables the source of the work breakdown structure classification to be identified. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constraint Association | General |
Constraints may be applied to a task's scheduled duration, start, or finish, by setting the IfcMetric.ReferencePath to the corresponding attribute on the IfcTaskTime entity. Figure 5.3.3.6.1.3.A indicates fixed duration of task with ConstraintGrade=HARD and Benchmark=EQUALTO such that changes to an assigned IfcConstructionResource.Usage.ScheduleWork should impact IfcConstructionResource.Usage.ScheduleUsage, and vice-versa. Figure 5.3.3.6.1.3.B indicates how to constrain the scheduled start date of the task. Depending on the ConstraintGrade and Benchmark the constraint may indicate different meanings as shown in Table 5.3.3.6.1.3.J.
Figure 5.3.3.6.1.3.C indicates how to constrain the scheduled finish date of the task. Depending on the ConstraintGrade and Benchmark the constraint may indicate different meanings as shown in Table 5.3.3.6.1.3.K.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Object Nesting | General |
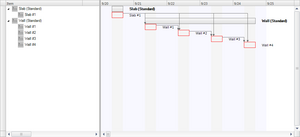
IfcTask may be contained within an IfcTask using the IfcRelNests relationship. An IfcTask may in turn nest other IfcTask, IfcProcedure or IfcEvent entities. Such nesting indicates decomposed level of detail. From IFC4 onwards it is required to have a summary task (root of all tasks), which is used to define a link to the work plan or work schedule. All subtasks of the summary tasks are then implicitly linked to this work plan or work schedule. Please note that the summary task is used for data organization and not meant to store typical task information as defined by the user. It is therefore recommended that the summary task is hidden from the user to avoid confusion. Please also note that IfcRelNests is used to show the dependency between regular tasks and recurring task definitions (please see the section about time and duration use definitions). As shown in Figure 5.3.3.6.1.3.D, the installation of a number of items of equipment within a particular space may be the subject of a single task which is identified as 'fix equipment in space 123'. IfcTask represents the occurrence of a work performance of a type of process in a construction plan. 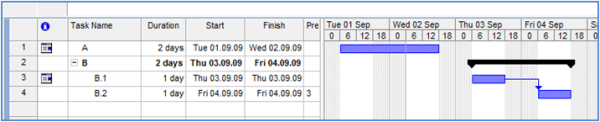 A task may nest other tasks as sub-items; the nesting relationship is modeled by IfcRelNests as shown in Figure 5.3.3.6.1.3.E. For example, the construction of a stud wall may be designated as a nesting task named 'install wall #1' including other tasks such as 'install dry wall', 'install studs', 'wall taping', and 'erect wall' as sub-processes. A value that indicates the relative tree view position of the task (in comparison to the tree view position of other tasks and the task hierarchy defined by IfcRelNests). The task order information that is used for viewing purposes is derived from the order defined by the IfcRelNests relationship and thus is independent of the logical task order defined through IfcRelSequence. The hierarchy and order defined through IfcRelNests enables to order the tasks in a tree view or list view structure. 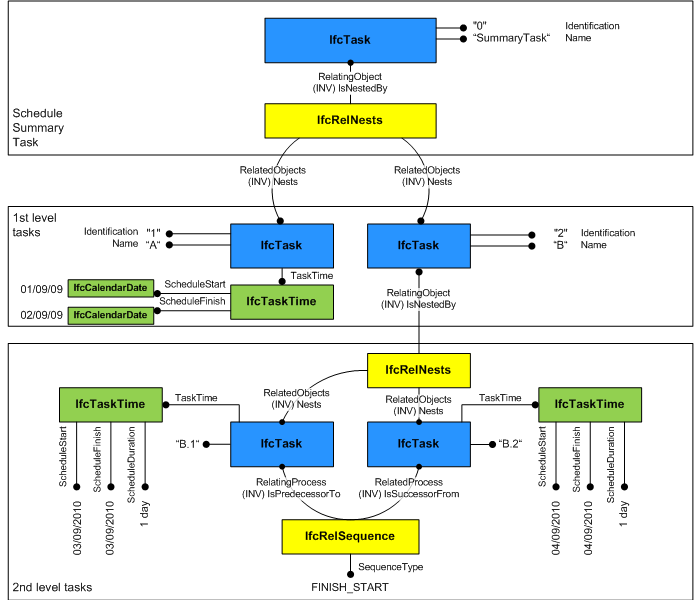 A top-level task is declared within the IfcProject using the IfcRelDeclares relationship. This concept can be applied to the following resources: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Object Typing | General |
The IfcTask defines the anticipated or actual occurrence of any task; common information about task types is handled by IfcTaskType. This concept can be applied to the following resources: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Process Assignment | General |
It is suggested to use the 'summary task' (root element of the task hierarchy that is required for task management purposes) to assign all subtask to a work plan or work schedule. Resources used by tasks are assigned by IfcRelAssignsToProcess. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Property Sets for Objects | General |
This concept can be applied to the following resources:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sequential Connectivity | General |
The relationship IfcRelSequence is used to indicate control flow. An IfcTask as a successor to an IfcTask indicates logical sequence how these tasks should be performed. IfcTask entities can be triggered or can trigger IfcEvent entities, which is also defined through the relationship IfcRelSequence. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5.3.3.6.7 Examples
5.3.3.6.8 Formal representation
ENTITY IfcTask
SUBTYPE OF (IfcProcess);
Status : OPTIONAL IfcLabel;
WorkMethod : OPTIONAL IfcLabel;
IsMilestone : IfcBoolean;
Priority : OPTIONAL IfcInteger;
TaskTime : OPTIONAL IfcTaskTime;
PredefinedType : OPTIONAL IfcTaskTypeEnum;
WHERE
CorrectPredefinedType : NOT(EXISTS(PredefinedType)) OR (PredefinedType <> IfcTaskTypeEnum.USERDEFINED) OR ((PredefinedType = IfcTaskTypeEnum.USERDEFINED) AND EXISTS(SELF\IfcObject.ObjectType));
HasName : EXISTS(SELF\IfcRoot.Name);
END_ENTITY;